- Android 培训
- 序言
- 1. Android入门基础:从这里开始
- 2. Android分享操作
- 3. Android多媒体
- 4. Android图像与动画
- 5. Android网络连接与云服务
- 6. Android联系人与位置信息
- 7. Android可穿戴应用
- 8. Android TV应用
- 9. Android企业级应用
- 10. Android交互设计
- 11. Android界面设计
- 12. Android用户输入
- 13. Android后台任务
- 14. Android性能优化
- 15. Android安全与隐私
- 16. Android测试程序
使用旧的APIs实现新API的效果
编写: spencer198711 - 原文:http://developer.android.com/training/backward-compatible-ui/older-implementation.html
这一课讨论了如何创建一个支持旧的设备并且与新的APIs接口相同的实现。
决定一个替代方案
在以向后兼容的方式使用较新的UI功能的时候,最具挑战的任务是为旧的平台版本决定一个解决方案。在很多情况下,使用旧的UI框架中的功能是有可能完成这些新的UI组件的。例如:
- Action Bar可以使用水平的包含图片按钮的LinearLayout来实现,这个在Activity中的LinearLayout作为自定义标题栏或者仅仅作为视图。下拉功能行为可以使用设备的菜单按钮来实现。
- Action Bar的tab页可以使用包含按钮的水平的LinearLayout,或者使用TabWidgetUI控件来实现。
- NumberPicker和Switch控件可以分别通过使用Spinner和ToggleButton控件来实现。
- ListPopupWindow和PopupMenu控件可以通过使用PopupWindow来实现。
为了往老的设备上向后移植UI组件,这些一般不是一刀切的解决方案。注意用户体验:在老的设备上,用户可能不熟悉新的界面设计模式和UI组件,思考一下如何使用熟悉的控件去实现相同的功能。在很多种情况下,这些通常不会被注意到,特别是在如果新的UI组件在应用程序的生态系统中是突出的(比如Action Bar),或者交互模型是非常简单和直观的(比如使用ViewPager去滑动界面)。
使用旧的APIs实现Tabs
你可以使用TabWidget和TabHost(尽管其中一个也可以使用水平方向的Button控件)去创建Action Bar Tabs的老的实现。可以在TabHelperEclair和CompatTabEclair的类中去实现,因为这些实现使用了不迟于Android 2.0(Eclair)的APIs。
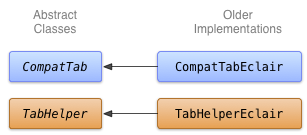
- 图1. Eclair版本上实现tabs的类图
CompatTabEclair在实例变量中保存了诸如tab文本和tab图标等tab属性,因为在老的版本中没有ActionBar.Tab对象去处理这些数据存储。
public class CompatTabEclair extends CompatTab {
// Store these properties in the instance,
// as there is no ActionBar.Tab object.
private CharSequence mText;
...
public CompatTab setText(int resId) {
// Our older implementation simply stores this
// information in the object instance.
mText = mActivity.getResources().getText(resId);
return this;
}
...
// Do the same for other properties (icon, callback, etc.)
}
TabHelperEclair利用了TabHost控件的方法去创建TabHost.TabSpec对象和tab的页面指示效果:
public class TabHelperEclair extends TabHelper {
private TabHost mTabHost;
...
protected void setUp() {
if (mTabHost == null) {
// Our activity layout for pre-Honeycomb devices
// must contain a TabHost.
mTabHost = (TabHost) mActivity.findViewById(
android.R.id.tabhost);
mTabHost.setup();
}
}
public void addTab(CompatTab tab) {
...
TabSpec spec = mTabHost
.newTabSpec(tag)
.setIndicator(tab.getText()); // And optional icon
...
mTabHost.addTab(spec);
}
// The other important method, newTab() is part of
// the base implementation.
}
现在你已经有了两种CompatTab和TabHelper的实现,一种是使用了新的APIs为了能够在Android 3.0或其后版本设备上能够运行,另一种则是使用了旧的APIs为了在Android 2.0或之前的设备上能够运行。下一课讨论在应用中使用这两种实现。